Understanding the distance between Earth and the Moon is a fascinating topic that has captivated scientists, astronomers, and enthusiasts alike for centuries. This celestial relationship plays a critical role in various natural phenomena, including tides, eclipses, and even the stability of Earth's climate. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of this distance, its significance, and how it has been measured over time.
The Moon, Earth's only natural satellite, maintains a relatively stable orbit around our planet. However, the distance between the two celestial bodies is not fixed. Instead, it varies due to the elliptical shape of the Moon's orbit. This fluctuation has significant implications for both scientific research and practical applications, such as space exploration and satellite technology.
This article aims to provide an in-depth analysis of the Earth-Moon distance, covering its historical context, measurement methods, and the impact it has on our planet. Whether you're a student, researcher, or simply curious about the universe, this guide will equip you with the knowledge you need to understand this vital astronomical relationship.
Read also:Mnemonic For Heart Murmurs A Comprehensive Guide For Accurate Diagnosis
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Earth-Moon Distance
- Historical Context of Lunar Distance Measurement
- The Average Distance Between Earth and the Moon
- Methods of Measuring the Distance
- Impact on Natural Phenomena
- Orbital Dynamics and Variations
- Future Exploration and Lunar Missions
- Scientific Importance of Lunar Distance
- Interesting Facts About Earth and the Moon
- Conclusion and Call to Action
Introduction to Earth-Moon Distance
The distance from Earth to the Moon, often referred to as the "Earth-Moon distance," is a fundamental concept in astronomy. This measurement is not just a number; it represents the intricate relationship between our planet and its natural satellite. The Moon's proximity influences various aspects of life on Earth, from the rhythm of the tides to the pull of gravity.
Throughout history, humans have sought to understand and measure this distance. Early civilizations relied on rudimentary methods, while modern science employs advanced technology to achieve precise measurements. Understanding the Earth-Moon distance is crucial for space exploration, satellite operations, and predicting celestial events.
Historical Context of Lunar Distance Measurement
Early Observations
For centuries, astronomers have been fascinated by the Moon's position relative to Earth. Ancient Greek mathematician Hipparchus made one of the earliest attempts to calculate the Earth-Moon distance around 150 BCE. Using geometric principles, he estimated the distance to be approximately 30 Earth radii, which is remarkably close to modern measurements.
Modern Techniques
Today, scientists use laser ranging technology to measure the Earth-Moon distance with unprecedented accuracy. By reflecting laser beams off retroreflectors placed on the Moon during the Apollo missions, researchers can determine the distance to within a few millimeters. This method has revolutionized our understanding of the Moon's orbit and its gradual movement away from Earth.
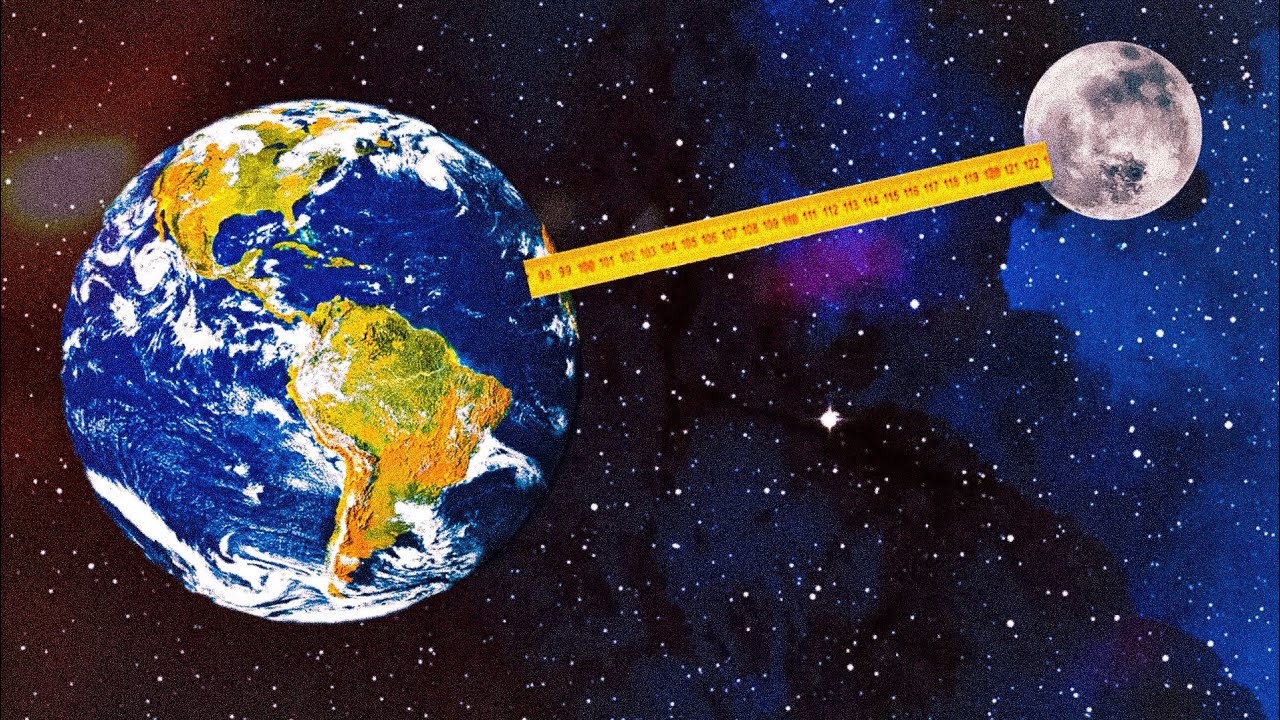
The Average Distance Between Earth and the Moon
The average distance from Earth to the Moon is about 384,400 kilometers (238,855 miles). However, this figure is an average because the Moon follows an elliptical orbit around Earth. At its closest point, known as perigee, the Moon is approximately 363,300 kilometers (225,623 miles) away. At its farthest point, called apogee, the distance increases to roughly 405,500 kilometers (251,966 miles).
Methods of Measuring the Distance
Parallax Method
One of the earliest scientific methods for measuring the Earth-Moon distance is the parallax method. By observing the Moon from two different locations on Earth, astronomers can calculate the angle difference and use trigonometry to determine the distance. This technique was widely used before the advent of modern technology.
Read also:Sweet Potato Air Fryer Carnivore Diet Recipe A Perfect Blend Of Flavor And Health
Laser Ranging
Laser ranging is currently the most accurate method for measuring the Earth-Moon distance. This technique involves firing lasers at retroreflectors on the Moon's surface and measuring the time it takes for the light to return. The precision of this method allows scientists to monitor subtle changes in the Moon's orbit over time.
Impact on Natural Phenomena
The Earth-Moon distance has a profound impact on various natural phenomena. For example, the gravitational pull of the Moon causes the tides in Earth's oceans. As the Moon orbits our planet, its gravitational influence creates a bulge in the water, resulting in high and low tides. Additionally, the Moon's position relative to Earth affects the occurrence of solar and lunar eclipses.
Orbital Dynamics and Variations
Elliptical Orbit
The Moon follows an elliptical orbit around Earth, meaning its distance varies throughout its monthly cycle. This variation is caused by the gravitational interactions between Earth, the Moon, and the Sun. The elliptical shape of the orbit also influences the Moon's apparent size and brightness in the night sky.
Gradual Recession
Interestingly, the Moon is gradually moving away from Earth at a rate of about 3.8 centimeters per year. This phenomenon is due to the tidal forces between the two celestial bodies. As the Moon recedes, Earth's rotation slows down, leading to longer days in the distant future.
Future Exploration and Lunar Missions
Understanding the Earth-Moon distance is essential for planning future lunar missions. Space agencies such as NASA and private companies like SpaceX are developing technologies to send humans back to the Moon. These missions aim to establish a sustainable presence on the lunar surface, paving the way for deeper exploration of the solar system.
Scientific Importance of Lunar Distance
Stability of Earth's Climate
The Moon's gravitational influence helps stabilize Earth's axial tilt, which is crucial for maintaining a stable climate. Without the Moon, Earth's tilt could vary significantly, leading to extreme climate fluctuations. This stability has allowed life to thrive on our planet for billions of years.
Research Opportunities
The Earth-Moon distance provides valuable opportunities for scientific research. By studying the Moon's orbit and its interaction with Earth, scientists can gain insights into the dynamics of the solar system and the formation of celestial bodies. This knowledge contributes to our broader understanding of the universe.
Interesting Facts About Earth and the Moon
- The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite and is about one-quarter the size of our planet.
- The Moon's gravity is only about 17% of Earth's gravity, making it a low-gravity environment.
- The Moon has no atmosphere, which means there is no weather or wind to erode its surface features.
- The Moon's surface is covered in dust, rocks, and craters, some of which are billions of years old.
- Humans first landed on the Moon in 1969 during NASA's Apollo 11 mission.
Conclusion and Call to Action
In conclusion, the distance from Earth to the Moon is a fascinating subject that touches on various aspects of science, history, and exploration. From ancient observations to modern laser ranging techniques, humanity's quest to understand this celestial relationship continues to evolve. The Earth-Moon distance plays a vital role in shaping our planet's environment and offers exciting opportunities for future research and exploration.
We encourage you to share this article with others who might be interested in learning more about the Earth-Moon relationship. If you have any questions or insights, feel free to leave a comment below. Additionally, explore other articles on our site to deepen your understanding of the universe and its mysteries.
Data sources: NASA, ESA, and other reputable scientific organizations.