Heart murmurs are often challenging to interpret, especially for medical students and early-career professionals. Using mnemonics for heart murmurs can significantly enhance your diagnostic skills and help you identify specific conditions effectively. This guide aims to provide you with valuable insights into mnemonics that simplify the process of understanding heart murmurs.
Heart murmurs are abnormal sounds heard during a heartbeat, which may indicate underlying cardiovascular issues. Whether you're a medical student, resident, or experienced clinician, mastering the art of auscultation is crucial. Mnemonics serve as valuable tools to simplify complex concepts, making it easier to remember key features of various heart murmurs.
By the end of this article, you will gain a comprehensive understanding of how mnemonics can assist in identifying different types of heart murmurs, their characteristics, and associated conditions. Let's dive in!
Read also:Who Is Trevor Wallace Dating The Ultimate Guide To His Love Life
Table of Contents
- What Are Heart Murmurs?
- Types of Heart Murmurs
- Mnemonics for Heart Murmurs
- Diagnosing Heart Murmurs
- Clinical Significance
- Common Heart Murmurs
- Tips for Accurate Diagnosis
- Case Studies
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What Are Heart Murmurs?
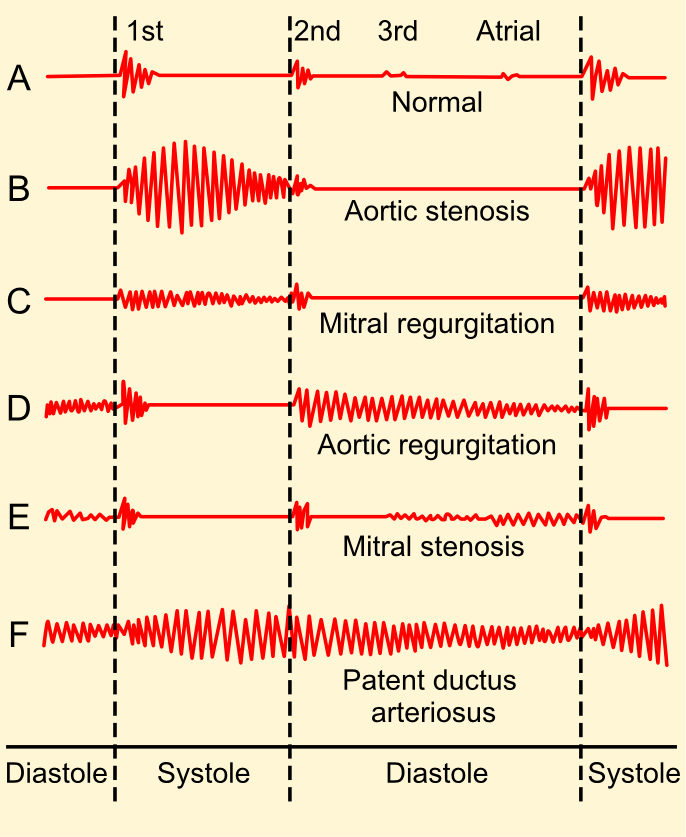
Heart murmurs are sounds produced by turbulent blood flow within the heart or blood vessels, detectable with a stethoscope during auscultation. These sounds can occur due to various reasons, including structural abnormalities, valvular disorders, or physiological changes. Understanding the basics of heart murmurs is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Heart murmurs can be classified as innocent or pathological. Innocent murmurs are harmless and commonly found in children, while pathological murmurs indicate underlying cardiovascular issues that require further investigation. Recognizing the difference between these two types is crucial for providing appropriate medical care.
Types of Heart Murmurs
Systolic Murmurs
Systolic murmurs occur during the contraction phase of the heart. They are further divided into:
- Ejection murmurs: Caused by turbulent flow through narrowed valves, such as aortic stenosis.
- Vibratory murmurs: Often associated with conditions like hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
Diastolic Murmurs
Diastolic murmurs occur during the relaxation phase of the heart. Common causes include:
- Aortic regurgitation: Backflow of blood into the left ventricle.
- Mitral stenosis: Narrowing of the mitral valve, leading to restricted blood flow.
Mnemonics for Heart Murmurs
Mnemonics can simplify the process of memorizing complex information about heart murmurs. Below are some popular mnemonics used in clinical practice:
Mnemonic for Systolic Murmurs
Use the mnemonic "ASAP" to remember common causes of systolic murmurs:
Read also:How Much Do Professional Cod Players Make A Comprehensive Guide To Call Of Duty Earnings
- A: Aortic stenosis
- S: Septal defects (e.g., ventricular septal defect)
- A: Atrial septal defect
- P: Pulmonic stenosis
Mnemonic for Diastolic Murmurs
For diastolic murmurs, remember "ARM":
- A: Aortic regurgitation
- R: Restrictive cardiomyopathy
- M: Mitral stenosis
Diagnosing Heart Murmurs
Accurate diagnosis of heart murmurs involves a combination of clinical assessment, imaging studies, and laboratory tests. Key steps include:
- Auscultation: Use a stethoscope to identify the timing, location, and quality of the murmur.
- Echocardiography: Provides detailed images of the heart's structure and function.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): Helps detect abnormalities in heart rhythm and electrical activity.
Clinical Significance
Understanding the clinical significance of heart murmurs is vital for providing appropriate care. Pathological murmurs may indicate serious conditions such as valvular heart disease, congenital defects, or cardiomyopathy. Early detection and management can prevent complications and improve patient outcomes.
Common Heart Murmurs
Aortic Stenosis
Aortic stenosis is a common cause of systolic murmurs, characterized by a high-pitched, crescendo-decrescendo sound heard best at the right second intercostal space. It is often associated with:
- Calcification of the aortic valve
- History of rheumatic fever
Mitral Regurgitation
Mitral regurgitation produces a holosystolic murmur heard best at the apex of the heart. It may result from:
- Myxomatous degeneration of the mitral valve
- Ischemic heart disease
Tips for Accurate Diagnosis
To ensure accurate diagnosis of heart murmurs, consider the following tips:
- Perform a thorough physical examination.
- Use advanced imaging techniques when necessary.
- Consult with specialists for complex cases.
Case Studies
Case 1: Aortic Stenosis
A 65-year-old male presents with exertional dyspnea and chest pain. On auscultation, a systolic murmur is heard at the right second intercostal space. Echocardiography confirms severe aortic stenosis, leading to a referral for valve replacement surgery.
Case 2: Mitral Stenosis
A 40-year-old female with a history of rheumatic fever reports difficulty breathing and fatigue. A diastolic murmur is detected during auscultation, and subsequent testing reveals mitral stenosis requiring intervention.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common causes of heart murmurs?
Common causes include valvular heart disease, congenital defects, and physiological changes. Innocent murmurs are frequently seen in children and are harmless.
How can mnemonics improve diagnostic accuracy?
Mnemonics simplify complex information, making it easier to remember key features of heart murmurs and their associated conditions.
Conclusion
Heart murmurs are an essential aspect of cardiovascular assessment, and using mnemonics can significantly enhance diagnostic accuracy. By understanding the types, causes, and clinical significance of heart murmurs, healthcare professionals can provide better care for their patients. We encourage you to:
- Share this article with colleagues and peers.
- Leave a comment with your thoughts or questions.
- Explore other articles on our website for more valuable insights.
Together, we can improve our diagnostic skills and contribute to better patient outcomes. Thank you for reading!