Understanding the distinction between gas and diesel fuel is crucial for maintaining your vehicle's performance and safety. Misfueling can lead to costly repairs and engine damage. This article will provide you with a detailed guide on how to identify the differences between these two types of fuel, ensuring you make the right choice every time.
Whether you're a new driver or a seasoned vehicle owner, knowing the difference between gas and diesel fuel can save you time, money, and frustration. From physical characteristics to usage scenarios, this guide will cover everything you need to know.
By the end of this article, you'll be equipped with the knowledge to confidently tell the difference between gas and diesel fuel, helping you avoid common mistakes that many drivers face.
Read also:Reserve Cowgirl Unveiling The Iconic Western Lifestyle
Table of Contents
- What is Gasoline?
- What is Diesel Fuel?
- Physical Differences Between Gas and Diesel Fuel
- Chemical Composition and Energy Content
- Usage Scenarios for Gas and Diesel Fuel
- The Risks of Misfueling
- How to Identify Gas and Diesel Fuel
- Proper Storage of Gas and Diesel Fuel
- Environmental Impact of Gas and Diesel Fuel
- Conclusion: Making the Right Choice
What is Gasoline?
Gasoline, often referred to simply as gas, is a refined petroleum product primarily used to fuel spark-ignition internal combustion engines. It is a volatile liquid that ignites easily and burns with a high-energy output, making it ideal for powering cars, motorcycles, and other small engines.
Gasoline is composed of hydrocarbons and additives designed to enhance performance, reduce emissions, and protect engine components. It is typically categorized by its octane rating, which measures its resistance to engine knock or premature detonation.
Key Characteristics:
- Highly flammable
- Lighter in weight compared to diesel
- Produces more noise and heat during combustion
What is Diesel Fuel?
Diesel fuel, on the other hand, is specifically designed for compression-ignition engines, which rely on high-pressure combustion to generate power. It is less volatile than gasoline and requires a higher temperature to ignite, making it more suitable for heavy-duty vehicles like trucks, buses, and generators.
Diesel fuel types:
- Regular diesel (used in most vehicles)
- Biodiesel (a renewable alternative)
- Ultra-low sulfur diesel (ULSD) for reduced emissions
Its higher energy density and efficiency make diesel fuel a popular choice for commercial and industrial applications.
Read also:Trisha Paytas Chicken Tenders A Sensational Recipe For Flavorful Delights
Physical Differences Between Gas and Diesel Fuel
Color and Smell
One of the easiest ways to differentiate between gas and diesel fuel is by observing their physical properties. Gasoline tends to have a lighter color, often clear or slightly yellowish, while diesel fuel is darker, with a more amber or brownish hue.
In terms of smell, gasoline has a sharp, distinct odor that is easily recognizable, whereas diesel fuel has a more oily, less pungent aroma.
Chemical Composition and Energy Content
Gasoline and diesel fuel differ significantly in their chemical makeup and energy content. Gasoline consists of shorter hydrocarbon chains, which contribute to its volatility and ease of ignition. Diesel fuel, on the other hand, contains longer hydrocarbon chains, resulting in higher energy density and efficiency.
Energy Content Comparison:
- Gasoline: Approximately 125,000 BTUs per gallon
- Diesel Fuel: Approximately 139,000 BTUs per gallon
This difference in energy content explains why diesel engines tend to be more fuel-efficient than gasoline engines.
Usage Scenarios for Gas and Diesel Fuel
Gasoline Usage
Gasoline is predominantly used in passenger vehicles, motorcycles, and small engines such as lawnmowers and generators. Its high volatility and ease of ignition make it ideal for applications requiring quick acceleration and responsiveness.
Diesel Fuel Usage
Diesel fuel powers heavy-duty vehicles and machinery, including trucks, buses, construction equipment, and agricultural vehicles. Its superior energy density and efficiency make it the preferred choice for applications requiring sustained power and torque.
The Risks of Misfueling
Misfueling occurs when the wrong type of fuel is used in a vehicle's engine. This can happen when gasoline is accidentally added to a diesel engine or vice versa. The consequences of misfueling can be severe, leading to engine damage, performance issues, and costly repairs.
Common Symptoms of Misfueling:
- Difficulty starting the engine
- Unusual noises during operation
- Loss of power or acceleration
It is essential to consult a professional mechanic immediately if you suspect misfueling has occurred.
How to Identify Gas and Diesel Fuel
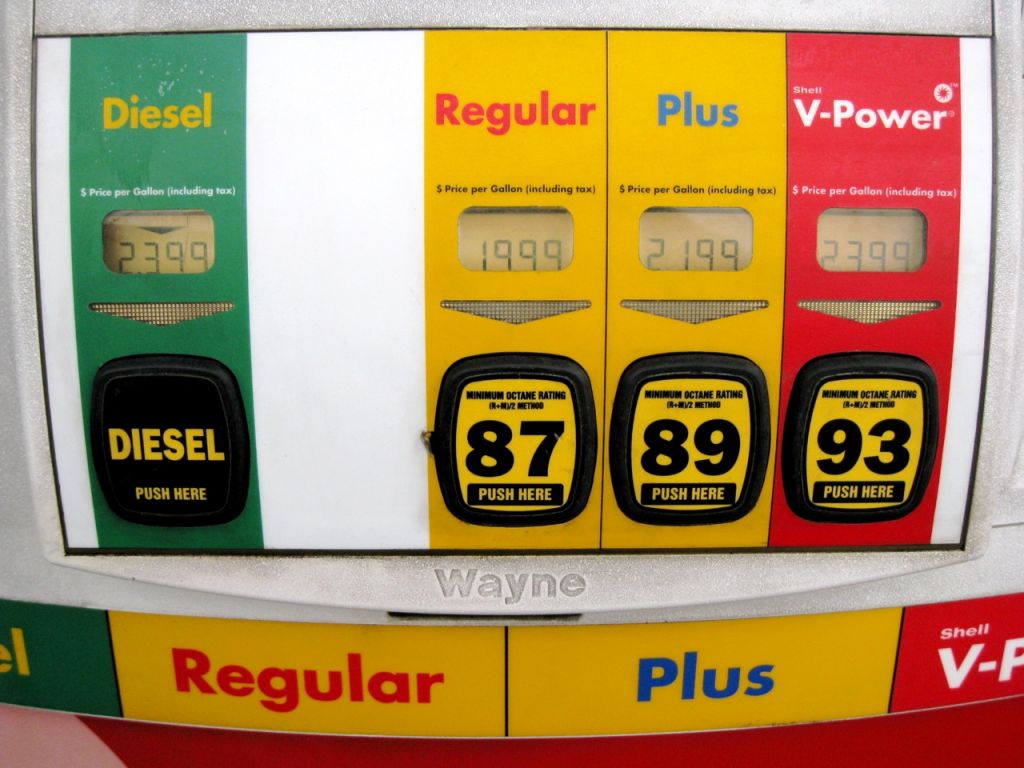
Labeling at the Pump
Gas stations often use clear labeling to help drivers distinguish between gas and diesel fuel. Look for signs indicating the type of fuel being dispensed, as well as color-coded nozzles and handles.
Key Indicators:
- Gasoline nozzles are smaller and fit only into gas vehicle tanks
- Diesel nozzles are larger and designed for diesel vehicle tanks
On-Vehicle Indicators
Modern vehicles often have labels near the fuel cap specifying the type of fuel required. Additionally, some vehicles feature locking mechanisms that prevent the insertion of the wrong nozzle.
Proper Storage of Gas and Diesel Fuel
Proper storage of gas and diesel fuel is critical to maintaining their quality and ensuring safe handling. Both fuels should be stored in approved containers, away from heat sources and direct sunlight.
Storage Tips:
- Use containers specifically designed for fuel storage
- Keep containers tightly sealed to prevent evaporation
- Store in a well-ventilated area, away from living spaces
Regularly inspect stored fuel for signs of contamination or degradation, and dispose of it properly if necessary.
Environmental Impact of Gas and Diesel Fuel
Both gasoline and diesel fuel have significant environmental implications. Gasoline combustion produces higher levels of carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides, contributing to air pollution and smog. Diesel fuel, while more efficient, emits particulate matter and sulfur dioxide, which can harm respiratory health.
Environmental Considerations:
- Use fuel-efficient vehicles to reduce emissions
- Explore alternative fuels like biodiesel and electric power
- Adopt eco-friendly driving habits to minimize fuel consumption
By making informed choices, drivers can help mitigate the environmental impact of fuel usage.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice
Telling the difference between gas and diesel fuel is an essential skill for every vehicle owner. By understanding their physical and chemical differences, usage scenarios, and potential risks, you can avoid costly mistakes and ensure optimal performance for your vehicle.
We encourage you to share this article with fellow drivers and leave a comment below if you have any questions or insights. For more informative guides on automotive care and maintenance, explore our other articles and stay updated on the latest industry developments.
Data Source: U.S. Energy Information Administration, Environmental Protection Agency, and leading automotive manufacturers.